There's a lot of misinformation circulating about electric vehicles. Some myths stem from outdated information, others from misunderstanding the technology, and some are deliberately spread to slow EV adoption. Let's examine and debunk the most common misconceptions with facts and data.
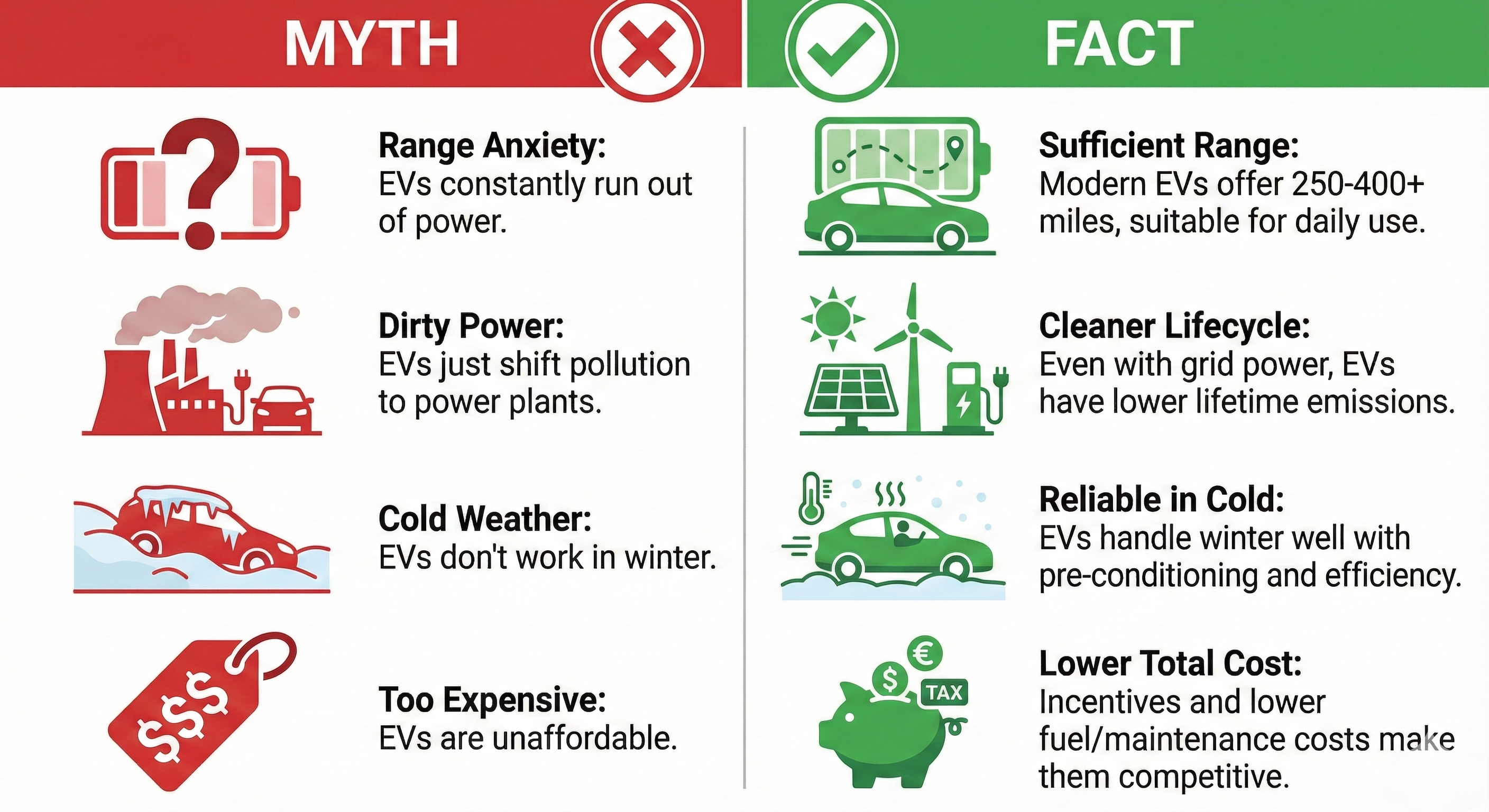
"EVs aren't really better for the environment"
EVs are significantly better for the environment
Lifecycle Emissions: Even when accounting for manufacturing and electricity generation, EVs produce 50-70% fewer emissions over their lifetime compared to gas vehicles.
Getting Cleaner: As the electrical grid incorporates more renewable energy, EVs automatically become cleaner without any changes to the vehicle.
Manufacturing Impact: Yes, battery production has environmental costs, but this is more than offset by the emissions saved during operation. The "break-even" point is typically reached within 1-2 years of driving.
Even with Coal: Studies show that even in regions heavily dependent on coal power, EVs still produce fewer total emissions than gas vehicles due to the superior efficiency of electric motors.
"EVs don't have enough range for daily use"
Modern EVs have more than enough range for most drivers
Average Daily Driving: The average American drives about 40 miles per day. Even entry-level EVs offer 200+ miles of range - 5x the daily average.
Modern Range: Many current EVs offer 250-350+ miles of range, comparable to many gas vehicles.
Home Charging Advantage: With home charging, you start every day with a "full tank," unlike gas cars where you need to detour to refuel.
Road Trips: Fast-charging networks make long-distance travel practical. A 20-30 minute charging stop every 200-300 miles aligns well with natural break times.
"EVs don't work in cold weather"
EVs work fine in cold weather, with some range reduction
Range Impact: Cold weather can reduce range by 20-40% in extreme conditions, but this still leaves plenty of range for daily driving.
Norway's Success: Norway, one of the coldest countries in Europe, has over 80% EV market share for new car sales. If EVs didn't work in cold weather, this wouldn't be possible.
Preconditioning Helps: Warming the cabin and battery while plugged in minimizes range loss and you start with a warm car.
No Starting Issues: Unlike gas cars, EVs don't have trouble starting in cold weather. No frozen fuel lines, dead batteries from cranking, or waiting for the engine to warm up.
"You'll need to replace the battery after a few years"
EV batteries last much longer than most people think
Warranty Protection: Federal law requires EV batteries to be warranted for at least 8 years/100,000 miles. Many manufacturers offer 8-10 years/150,000+ mile warranties.
Real-World Data: Studies of Tesla vehicles show an average of only 10% capacity loss after 200,000 miles. Most batteries will outlast the vehicle.
Gradual Degradation: Batteries don't suddenly fail - they gradually lose capacity over many years. Even with some degradation, the car remains perfectly usable.
Decreasing Costs: Battery costs have dropped 89% in the past decade and continue to fall, making future replacements much more affordable.
"Charging takes too long"
Charging is actually more convenient than gas for daily use
Home Charging: Plug in at night, wake up with a full charge. Total "effort" time: 5 seconds to plug in. No trips to gas stations for daily driving.
Fast Charging: Modern DC fast chargers can add 200+ miles of range in 20-30 minutes - perfect for a meal or restroom break on road trips.
Time Perspective: While charging takes longer than pumping gas, you're not standing there waiting. You're doing other things while the car charges.
Improving Technology: Charging speeds continue to improve, with some new EVs capable of adding 100 miles in just 5 minutes.
"The electrical grid can't handle EVs"
The grid has plenty of capacity, especially with smart charging
Off-Peak Charging: Most EV charging happens at night when grid demand is lowest. This actually helps utilities use existing capacity more efficiently.
Gradual Transition: EV adoption is happening over decades, giving utilities time to upgrade infrastructure as needed.
Grid Studies: Multiple studies have shown that the grid can handle widespread EV adoption with modest upgrades, especially with smart charging management.
Vehicle-to-Grid: Future EVs may actually help stabilize the grid by providing energy storage and load balancing.
"EV batteries are dangerous and catch fire easily"
EVs are statistically safer from fires than gas vehicles
Fire Statistics: Gas vehicles catch fire at a rate of about 1,530 per 100,000 sold. EVs catch fire at a rate of about 25 per 100,000 - over 60 times less likely.
Media Bias: EV fires get disproportionate media coverage because they're novel, while the thousands of gas car fires annually go unreported.
Safety Features: EV batteries have multiple safety systems including thermal management, crash protection, and automatic shutdown mechanisms.
No Gasoline: EVs don't carry gallons of highly flammable liquid, eliminating a major fire risk present in gas vehicles.
"EVs are too expensive"
Total cost of ownership is often lower than gas vehicles
Upfront Costs: While some EVs have higher purchase prices, incentives can reduce this gap significantly (up to $7,500 federal + state incentives).
Operating Costs: EVs cost 3-5x less per mile to fuel and have 40% lower maintenance costs, saving thousands over the vehicle's lifetime.
Price Parity: Many EVs are already at or near price parity with comparable gas vehicles, especially when considering incentives.
Resale Value: EVs are holding their value well, and as gas vehicles become less desirable, EV resale values are expected to remain strong.
"EVs rely on rare earth metals and unethical mining"
The situation is complex but improving rapidly
Not Actually "Rare": Despite the name, rare earth elements aren't particularly rare. Many modern EV batteries (like LFP) don't use them at all.
Cobalt Reduction: Battery manufacturers are rapidly reducing or eliminating cobalt use. Many new batteries use little to no cobalt.
Ethical Sourcing: Major manufacturers are implementing strict ethical sourcing requirements and supply chain transparency.
Recycling: Battery recycling programs are being developed to recover and reuse materials, reducing mining needs.
Comparison: Oil extraction and refining also have significant environmental and ethical issues that are often overlooked in this debate.
"EVs are slow and boring to drive"
EVs offer superior performance and driving dynamics
Instant Torque: Even basic EVs accelerate faster than most gas cars due to instant torque delivery.
Performance EVs: High-performance EVs can match or exceed supercars in acceleration, with 0-60 times under 3 seconds.
Handling: Low center of gravity from floor-mounted batteries provides excellent handling and stability.
Driver Engagement: The immediate response and one-pedal driving create a more engaging, connected driving experience.
The Truth About EVs
Many EV myths stem from outdated information, misunderstandings, or deliberate misinformation. The reality is that modern electric vehicles are practical, affordable, environmentally beneficial, and enjoyable to drive.
As with any major technology transition, there are legitimate questions and concerns. However, the facts show that EVs are ready for mainstream adoption and offer significant advantages over traditional vehicles.
Don't let myths and misinformation prevent you from experiencing the benefits of electric driving. Do your own research, test drive an EV, and make an informed decision based on facts, not fiction.




























