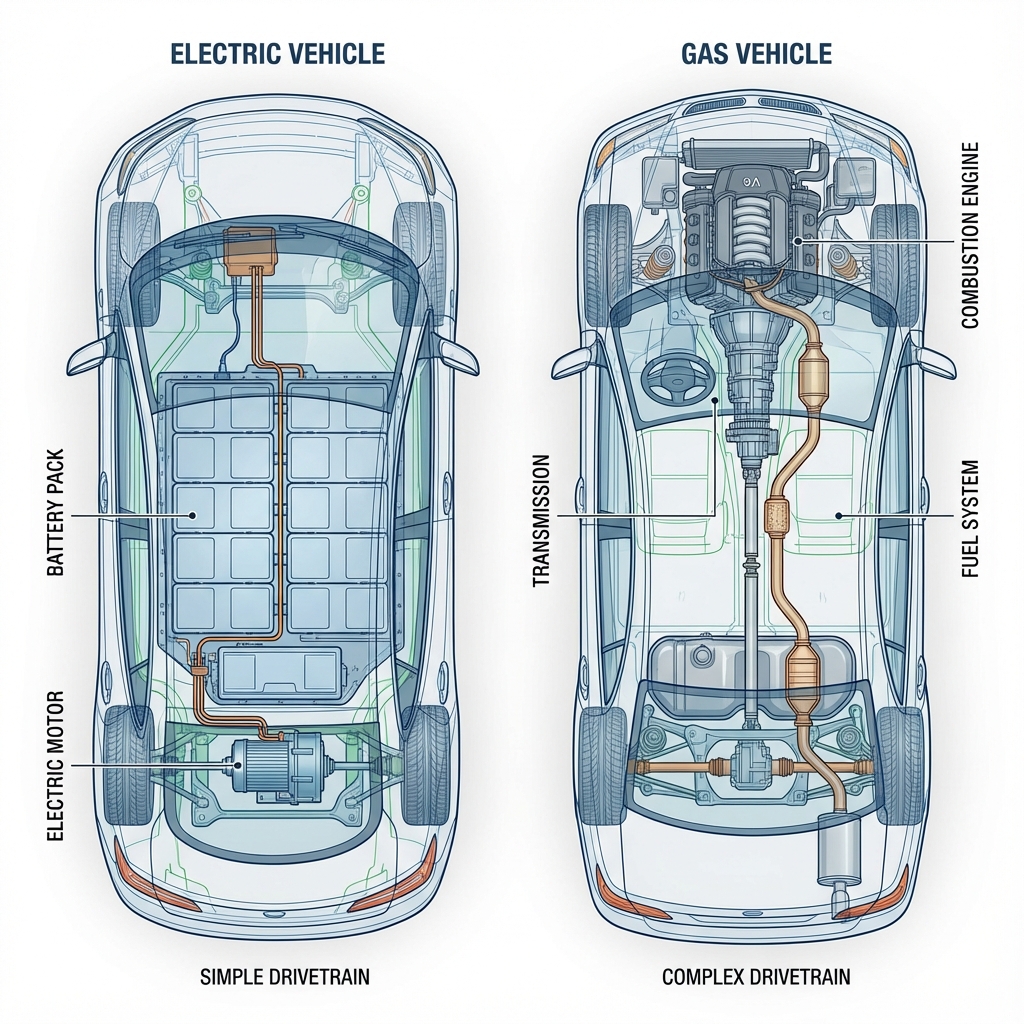
Peruserojen ymmärtäminen sähkö- ja polttomoottoriajoneuvojen välillä auttaa sinua tekemään tietoon perustuvan päätöksen. Verrataan näitä teknologioita kaikilla keskeisillä ulottuvuuksilla.
Pikainen Vertailutaulukko
| Feature | Electric Vehicle | Gas/Diesel Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| Energianlähde | Sähkö verkosta | Bensiini tai dieselpolttoaine |
| Tehokkuus | 85-90% | 20-30% |
| Polttoainekustannus/Maili | $0.03-0.05 | $0.12-0.18 |
| Huolto | Minimaalinen (40% alhaisemmat kulut) | Säännölliset öljynvaihdot, monimutkainen |
| Liikkuvat Osat | ~20 voimansiirrossa | ~2,000 voimansiirrossa |
| Kiihtyvyys | Välitön vääntö, erittäin nopea | Asteittainen tehonmuodostus |
| Melutaso | Lähes äänetön | Moottorin ja pakoputken meteli |
| Päästöt | Ei pakokaasupäästöjä | CO2, NOx, hiukkaset |
| Tankkausaika | Kotona: yön yli; Nopea: 20-30 min | 5 minuuttia |
| Toimintamatka | 200-400+ mailia | 300-500+ mailia |
Sähköauton Edut
- ✓ Paljon alhaisemmat käyttökustannukset
- ✓ Ylivoimainen tehokkuus
- ✓ Välitön kiihtyvyys
- ✓ Minimaalinen huolto
- ✓ Nollapäästöt
- ✓ Hiljainen toiminta
- ✓ Kotilatauksen mukavuus
- ✓ Parempi ympäristölle
Bensiini/Diesel Edut
- ✓ Nopeampi tankkaus
- ✓ Pidempi toimintamatka (tyypillisesti)
- ✓ Kattava tankkausinfrastruktuuri
- ✓ Alhaisempi hankintahinta (usein)
- ✓ Tuttu teknologia
- ✓ Parempi erittäin pitkille matkoille
Tuomio
Useimmille kuljettajille sähköautot tarjoavat ylivoimaisen päivittäisen ajökokemuksen, alhaisemmat kustannukset ja paremman ympäristövaikutuksen. Bensiiniautoilla on edelleen etuja tietyissä käyttötapauksissa, kuten usein toistuvassa pitkän matkan matkustamisessa ilman latausinfrastruktuuria, mutta tämä kuilu kurotaan umpeen nopeasti latausverkostojen laajentuessa ja sähköautojen toimintamatkan kasvaessa.




























