Sähköauton lataaminen voi aluksi tuntua monimutkaiselta, mutta se on itse asiassa melko suoraviivaista, kun opit perusteet. On olemassa kolme päälataustasoa ja useita liitintyyppejä, joita käytetään eri alueilla ja eri valmistajien toimesta.
Lataustasot Selitettynä
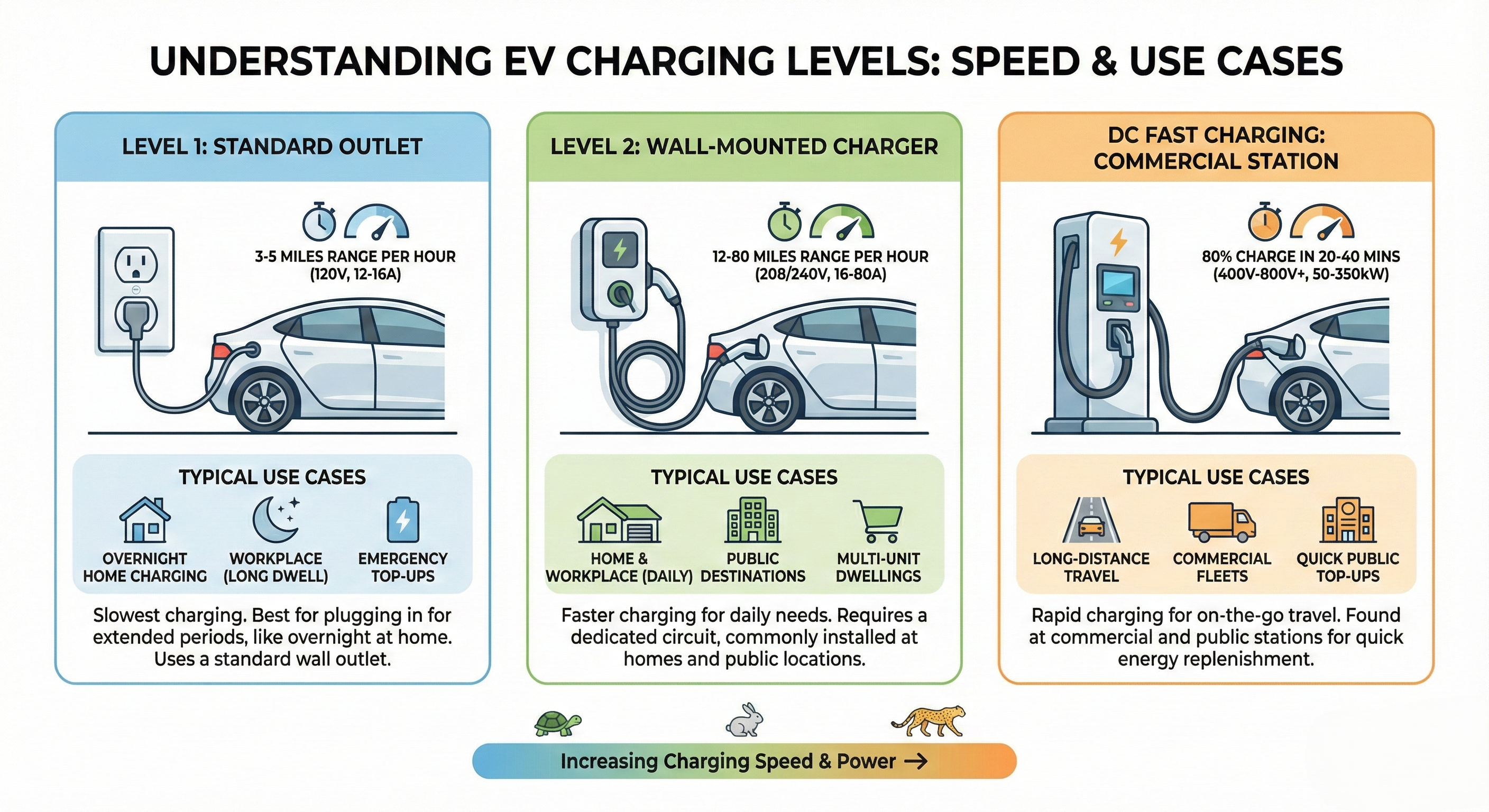
Taso 1 Lataus (120V AC)
What is it?: Lataaminen tavallisesta kotitalouspistorasiasta (120V Pohjois-Amerikassa).
Specifications:
- Teho: 1.4-1.9 kW
- Nopeus: 3-5 mailia toimintamatkaa tunnissa
- Täysi lataus: 40-50+ tuntia
Best For:
- Yön yli lataaminen alhaisille päivittäisille kilometreille
- Hätävaralataus
- PHEV:t pienillä akuilla
- Ei vaadi asennusta
Taso 2 Lataus (240V AC)
What is it?: Lataaminen 240V pistorasiasta (kuten kuivausrummun pistorasia) tai omistautuneesta sähköautolaturista.
Specifications:
- Teho: 3.3-19.2 kW (tyypillisesti 7.2-11 kW)
- Nopeus: 12-60 mailia toimintamatkaa tunnissa
- Täysi lataus: 4-10 tuntia
Best For:
- Kotilataus (yleisin)
- Työpaikkalataus
- Julkiset pysäköintialueet
- Yön yli tai päivittäinen lataus
Note: Tämä on ihanteellinen useimmille sähköauton omistajille. Riittävän nopea päivittäisiin tarpeisiin, hellävarainen akulle ja edullinen asentaa.
DC Pikalataus (DCFC)
What is it?: Korkeatehoinen DC-lataus, joka ohittaa auton sisäisen laturin.
Specifications:
- Teho: 50-350 kW
- Nopeus: 100-200+ mailia 15-30 minuutissa
- 80% lataus: 20-40 minuuttia
Best For:
- Maantiematkat ja pitkän matkan matkustaminen
- Nopeat lisäykset tarvittaessa
- Kaupalliset/kalustoajoneuvot
- Kun et voi ladata kotona
Important: Lataus hidastuu merkittävästi 80% jälkeen akun terveyden suojelemiseksi. Nopeinta latausta varten suunnittele lataavasi 10-80% välillä.
Liitintyypit Alueittain
Pohjois-Amerikka
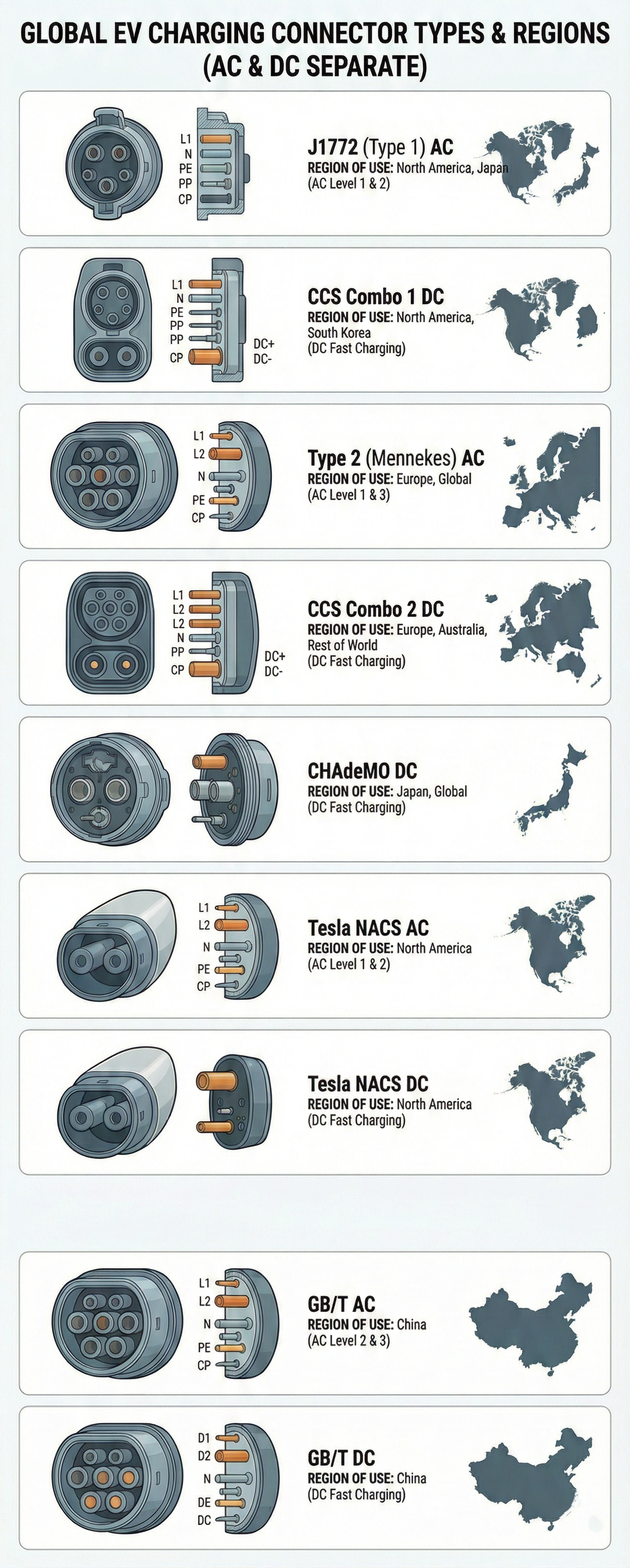
J1772 (Tyyppi 1)
Use: Taso 1 ja Taso 2 AC lataus
Compatibility: Kaikki ei-Tesla sähköautot Pohjois-Amerikassa
Power: Jopa 19.2 kW (tyypillisesti 7.2 kW)
CCS Combo 1 (CCS1)
Use: DC pikalataus
Compatibility: Useimmat ei-Tesla sähköautot Pohjois-Amerikassa
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Yhdistää J1772:n DC-pinneillä yhdeksi yleisportiksi
Tesla NACS (North American Charging Standard)
Use: Kaikki lataustasot (AC ja DC)
Compatibility: Tesla-ajoneuvot, tulossa alan standardiksi
Power: Jopa 250 kW (Supercharger V3)
Note: Ford, GM ja muut ottavat käyttöön NACS:n tulevissa ajoneuvoissa
CHAdeMO
Use: DC pikalataus
Compatibility: Nissan Leaf, vanhemmat japanilaiset sähköautot
Power: Jopa 62.5 kW (jotkut asemat jopa 100 kW)
Note: Poistumassa käytöstä CCS:n hyväksi
Eurooppa
Tyyppi 2 (Mennekes)
Use: Taso 2 AC lataus
Compatibility: Kaikki sähköautot Euroopassa
Power: Jopa 43 kW (tyypillisesti 7-22 kW)
Note: Eurooppalainen standardi AC-lataukselle
CCS Combo 2 (CCS2)
Use: DC pikalataus
Compatibility: Kaikki modernit sähköautot Euroopassa
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Yhdistää Tyyppi 2:n DC-pinneillä, eurooppalainen standardi
Latausnopeuteen Vaikuttavat Tekijät
Ajoneuvon Rajoitukset
- • Sisäisen laturin kapasiteetti (AC-lataukselle)
- • Maksimi DC-latausnopeus (ajoneuvokohtainen)
- • Akun lämpötila (kylmä = hitaampi)
- • Varaustila (hidastuu 80% jälkeen)
Laturin Rajoitukset
- • Laturin teho (kW luokitus)
- • Jaetut piirit (teho jaetaan autojen kesken)
- • Verkkokapasiteetti sijainnissa
- • Laturin kunto ja huolto
Key Point: Latausnopeutesi rajoittuu siihen kumpi on alhaisempi - ajoneuvosi maksimilatausnopeus tai laturin teho. 350 kW laturi ei lataa ajoneuvoa, jonka maksiminopeus on 50 kW, yhtään nopeammin kuin 50 kW laturi.
Latauskäyrän Ymmärtäminen
DC-pikalataus ei ylläpidä huippunopeutta koko session ajan. Sen sijaan se noudattaa "latauskäyrää":
Pro Tip: Nopeinta maantiematkalatausta varten, suunnittele lataavasi 10-20%:sta 80%:iin. Viimeiset 20% vie melkein yhtä kauan kuin ensimmäiset 80%, joten on tehokkaampaa pysähtyä useammin ja ladata 80%:iin kuin odottaa 100%:ia.
Pikaviite
Päivittäinen Lataus: Taso 2 kotona (7-11 kW) - kytke yöksi
Maantiematkat: DC Pikalataus (50-350 kW) - 20-30 minuutin pysähdykset
Hätätilanne: Taso 1 mistä tahansa pistorasiasta - hidas mutta toimii missä vain
Pohjois-Amerikka: J1772 (AC) + CCS1 tai NACS (DC)
Eurooppa: Tyyppi 2 (AC) + CCS2 (DC)




























