Lyginant elektromobilius su benzininiais ir dyzeliniais automobiliais reikia suprasti skirtingus energijos vienetus ir efektyvumo rodiklius. Išskaidykime skaičius prasmingam palyginimui.
Energijos Kiekio Palyginimas
EPA Ekvivalentiškumo Standartas
EPA nustatė, kad 8.9 kWh elektros = 1 litrui benzino (33.7 kWh = 1 galonui) pagal energijos kiekį. Tai naudojama apskaičiuoti MPGe (mylios per galoną ekvivalentas) elektromobiliams.
Elektra (kWh)
8.9 kWh
= 1 litro benzino ekvivalentas
Tiesiogiai naudojama elektros variklio
Benzinas
1 litras
= 8.9 kWh energijos
Turi būti sudegintas variklyje
Dyzelinas
1 litras
= 10 kWh energijos
~12% daugiau energijos nei benzinas
Efektyvumo Skirtumas
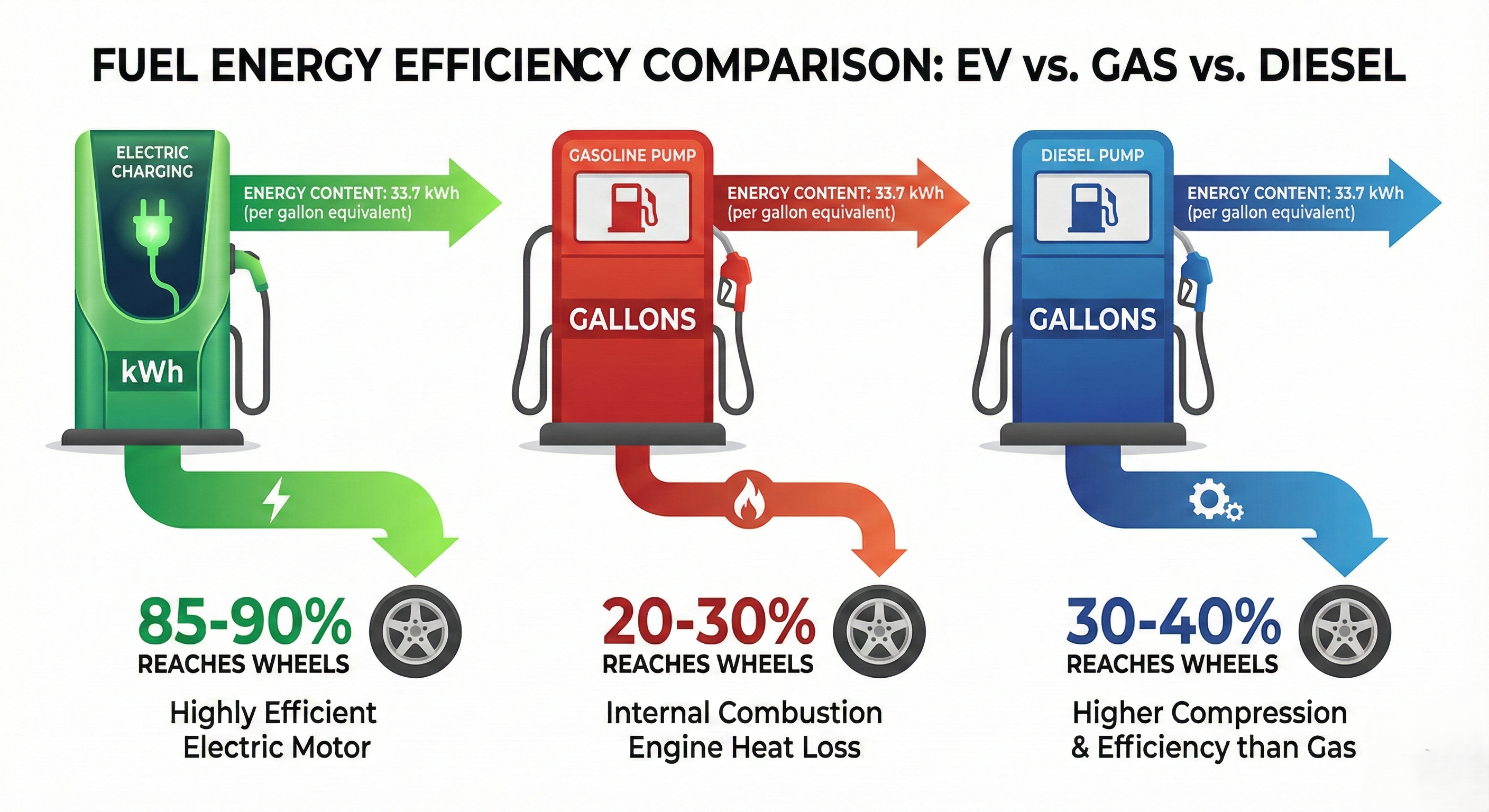
Štai esminis skirtumas: Turėti energiją yra viena - efektyviai ją panaudoti yra kas kita. Elektros varikliai yra dramatiškai efektyvesni nei vidaus degimo varikliai.
Elektromobiliai: 85-90% Efektyvumas
Elektros varikliai konvertuoja 85-90% elektros energijos į judėjimą. Labai mažai prarandama kaip šiluma.
Energijos Srautas (100 kWh iš baterijos):
- • 85-90 kWh → Suka ratus (judėjimas)
- • 10-15 kWh → Prarandama kaip šiluma ir kiti nuostoliai
Benzininiai Automobiliai: 20-30% Efektyvumas
Benzininiai varikliai iššvaisto 70-80% kuro energijos kaip šilumą. Tik 20-30% iš tikrųjų judina automobilį.
Energijos Srautas (100 kWh iš benzino):
- • 20-30 kWh → Suka ratus (judėjimas)
- • 70-80 kWh → Iššvaistoma kaip šiluma (išmetimas, aušinimas, trintis)
Dyzeliniai Automobiliai: 30-40% Efektyvumas
Dyzeliniai varikliai yra efektyvesni už benzininius, bet vis tiek iššvaisto didžiąją dalį energijos kaip šilumą.
Energijos Srautas (100 kWh iš dyzelino):
- • 30-40 kWh → Suka ratus (judėjimas)
- • 60-70 kWh → Iššvaistoma kaip šiluma
Apibendrinimas: Kad nuvažiuotumėte tą patį atstumą, jums reikia 3-4 kartus daugiau energijos iš benzino ar dyzelino nei iš elektros. Todėl EV yra daug pigesni "kuru".
Realus Pavyzdys: 500 km Važiavimas
Elektromobilis
Efektyvumas: 18 kWh/100km
Reikalinga energija: 90 kWh
Kaina po €0.20/kWh: €18.00
€18.00
Benzininis Automobilis
Efektyvumas: 8 L/100km
Reikalingas kuras: 40 litrų
Kaina po €1.50/L: €60.00
€60.00
Dyzelinis Automobilis
Efektyvumas: 6 L/100km
Reikalingas kuras: 30 litrų
Kaina po €1.40/L: €42.00
€42.00
Sutaupymas: EV kainuoja 70% pigiau nuvažiuoti tą patį atstumą nei benzinu ir 57% pigiau nei dyzelinu. Nuvažiuojant 20,000 km per metus, tai yra €1,680-960 kasmetinis sutaupymas vien kurui.
Suprantant MPGe
Kas yra MPGe?
MPGe (Miles Per Gallon equivalent) leidžia palyginti EV efektyvumą su benzininiais automobiliais naudojant pažįstamą matą (JAV). Tai atsako į klausimą: "Jei šis EV naudotų benziną, koks būtų jo MPG?"
Formulė:
MPGe = (Nuvažiuotos mylios ÷ sunaudotos kWh) × 33.7
Pavyzdiniai EV MPGe Reitingai
- • Tesla Model 3: 132 MPGe
- • Hyundai Ioniq 6: 140 MPGe
- • Ford Mustang Mach-E: 93 MPGe
- • Rivian R1T: 70 MPGe
Palyginami Benzininiai Automobiliai
- • Honda Civic: 36 MPG
- • Toyota Camry: 32 MPG
- • Ford Explorer: 24 MPG
- • Ford F-150: 22 MPG
Išvada: Net mažiausiai efektyvūs EV turi MPGe reitingus 2-3 kartus didesnius nei palyginami benzininiai automobiliai.
Metinių Kuro Išlaidų Palyginimas
Remiantis 20,000 km per metus
| Vehicle Type | Efficiency | Fuel Price | Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efektyvus EV | 15 kWh/100km | €0.20/kWh | €600 |
| Vidutinis EV | 20 kWh/100km | €0.20/kWh | €800 |
| Efektyvus Benzininis | 6 L/100km | €1.50/L | €1,800 |
| Vidutinis Benzininis | 8 L/100km | €1.50/L | €2,400 |
| Dyzelinis | 6 L/100km | €1.40/L | €1,680 |
| SUV/Visureigis Benzininis | 12 L/100km | €1.50/L | €3,600 |
5 Metų Sutaupymas: Vidutinis EV sutaupo €5,000-14,000 kurui lyginant su benzininiais automobiliais per 5 metus (100,000 km). Tai reikšminga suma, padengianti didesnę pradinę kainą.
Poveikis Aplinkai
Be kainos, efektyvumo skirtumas turi didelę įtaką aplinkai. Mažiau energijos reiškia mažiau emisijų, net įskaičiuojant elektros gamybą.
Elektra (ES Vidurkis)
~50-100 g CO₂/km
Įskaitant elektros gamybą
Benzinas
~200-250 g CO₂/km
Tiesioginės išmetimo emisijos
Dyzelinas
~180-230 g CO₂/km
Tiesioginės išmetimo emisijos
Pastaba: Elektros tinklui tampant švaresniam su daugiau atsinaujinančios energijos, EV automatiškai tampa dar švaresni. Benzino ir dyzelino emisijos išlieka pastovios.
Apibendrinimas
Energijos Efektyvumas: EV yra 3-4x efektyvesni nei vidaus degimo automobiliai
Kuro Kaina: Elektra kainuoja 3-5x mažiau nuvažiuoti kilometrą nei benzinas ar dyzelinas
Metinis Sutaupymas: €800-1,500+ per metus kurui vidutiniam vairuotojui
Poveikis Aplinkai: 40-60% mažesnės emisijos, mažėjančios tinklui švarėjant
MPGe: Dauguma EV pasiekia 90-140 MPGe ekvivalentą




























