Automobiļu industrija pāriet caur dažādiem elektrifikācijas posmiem. Izpratne par atšķirībām starp tradicionālajiem benzīna auto, hibrīdiem, uzlādējamiem hibrīdiem un pilnībā elektriskajiem auto palīdz izvēlēties pareizo variantu.
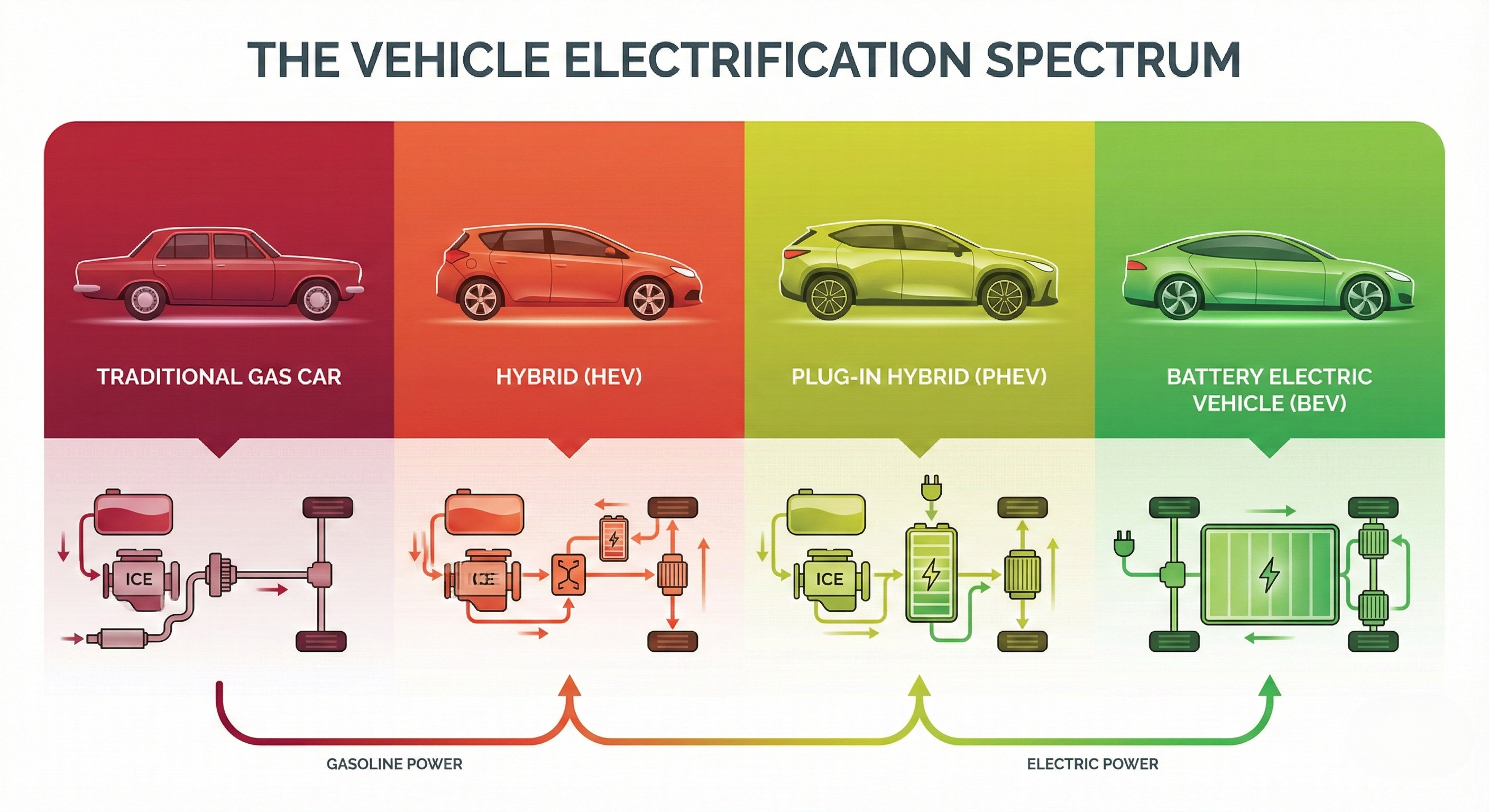
1. Tradicionālie Benzīna/Dīzeļa Auto
Kā Tas Darbojas
Iekšdedzes dzinējs sadedzina benzīnu vai dīzeļdegvielu, lai radītu jaudu. Nav elektrisko komponentu piedziņai.
- 100% darbināms ar benzīnu/dīzeli
- 20-30% efektivitāte
- Regulāra uzpilde degvielas stacijās
- Augstākās emisijas
2. Hibrīda Elektriskie Transportlīdzekļi (HEV)
Kā Tas Darbojas
Apvieno benzīna dzinēju ar nelielu elektromotoru un bateriju. Nevar pieslēgt rozetei - baterija uzlādējas tikai ar reģeneratīvo bremzēšanu un dzinēju.
Examples: Toyota Prius, Honda Accord Hybrid, Ford Maverick Hybrid
- 30-50% labāka degvielas ekonomija nekā benzīna auto
- Nav nepieciešama uzlāde
- Elektromotors palīdz benzīna dzinējam
- Joprojām nepieciešama visa benzīna auto apkope
3. Uzlādējamie Hibrīda Elektriskie Transportlīdzekļi (PHEV)
Kā Tas Darbojas
Lielāka baterija un elektromotors nekā HEV. Var pieslēgt uzlādei. Brauc ar elektrību 30-80 km, tad pārslēdzas uz benzīna dzinēju.
Examples: Toyota RAV4 Prime, Jeep Wrangler 4xe, Ford Escape PHEV, Volvo XC60 Recharge
- Tikai elektriskais nobraukums: 30-80 km
- Benzīna dzinējs garākiem braucieniem
- Labākais no abām pasaulēm daudziem vadītājiem
- Joprojām ir sarežģīta benzīna dzinēja apkope
4. Bateriju Elektriskie Transportlīdzekļi (BEV)
Kā Tas Darbojas
Darbojas pilnībā ar baterijas enerģiju. Nav benzīna dzinēja vispār. Jāpieslēdz uzlādei. Nulle emisiju.
Examples: Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, Ford Mustang Mach-E, Chevrolet Bolt, Hyundai Ioniq 5
- Nobraukums: 320-640+ km
- Nulle izpūtēja emisiju
- Zemākās ekspluatācijas izmaksas
- Nepieciešama minimāla apkope
- Nepieciešama piekļuve uzlādei
Salīdzinājuma Tabula
| Iezīme | HEV | PHEV | BEV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Var Pieslēgt? | Nē | Jā | Jā (obligāti) |
| Elektriskais Nobraukums | 1-3 km | 30-80 km | 320-640+ km |
| Ir Benzīna Dzinējs? | Jā | Jā | Nē |
| Apkope | Augsta | Augsta | Zema |
| Emisijas | Zemākas nekā benzīnam | Ļoti zemas (ja uzlādēts) | Nulle izpūtēja |
Kurš ir Piemērots Jums?
HEV: Labāka degvielas ekonomija nekā benzīnam, nav nepieciešama uzlādes infrastruktūra, pazīstama uzpilde
PHEV: Elektrība ikdienas braukšanai, benzīns gariem braucieniem, pārejas variants tiem, kas nav pārliecināti par pilnu elektroauto
BEV: Zemākās ekspluatācijas izmaksas, labākais videi, labākā braukšanas pieredze, nepieciešama piekļuve uzlādei




























