Разбирањето на полнењето на ЕВ може да изгледа комплицирано на почеток, но всушност е прилично едноставно штом ги научите основите. Постојат три главни нивоа на полнење и неколку типови на конектори кои се користат во различни региони и производители.
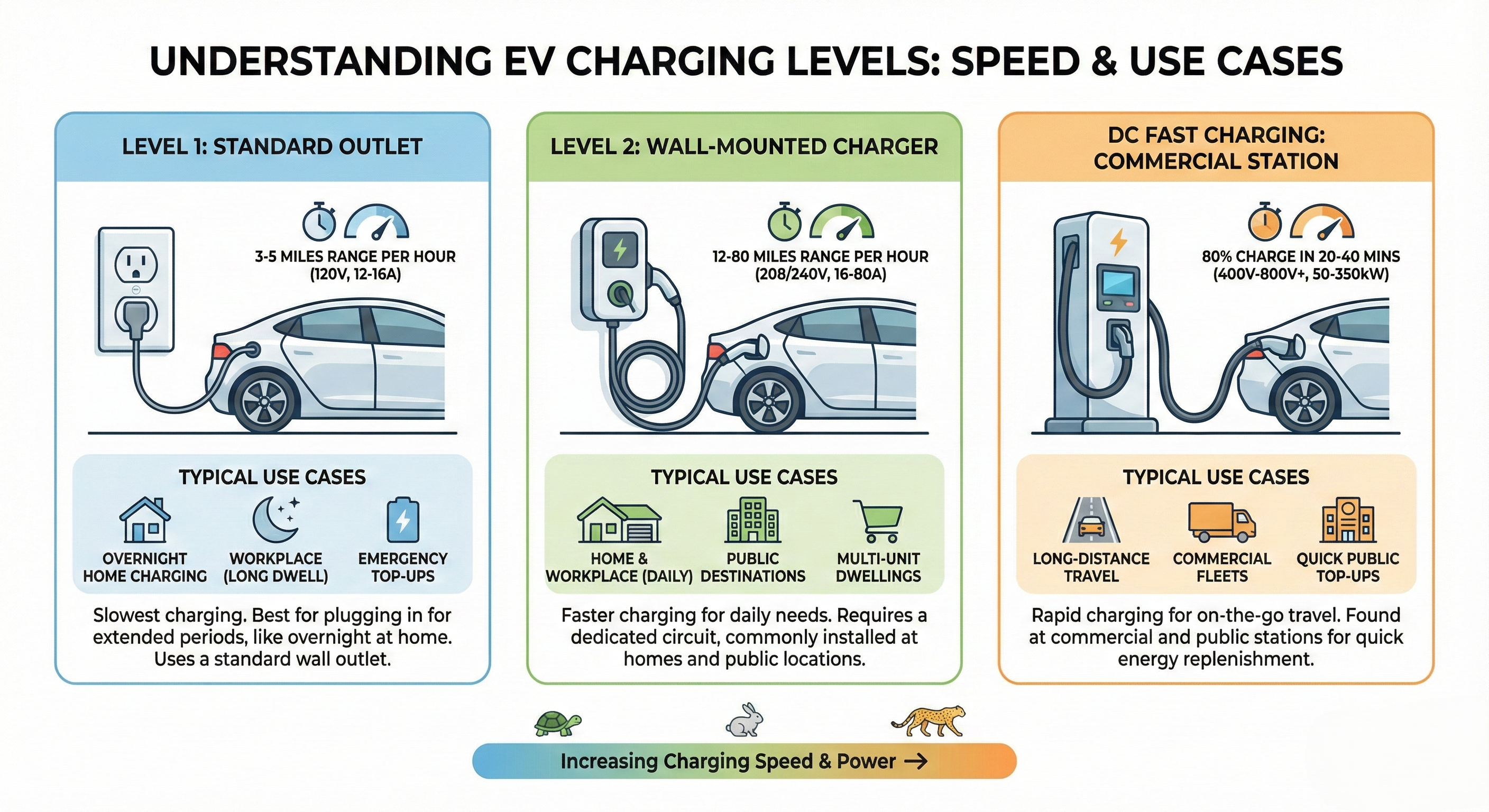
Објаснување на Нивоата на Полнење
Ниво 1 Полнење (120V AC)
What is it?: Полнење од стандарден домашен штекер (120V во Северна Америка).
Specifications:
- Моќност: 1.4-1.9 kW
- Брзина: 3-5 милји досег на час
- Целосно полнење: 40-50+ часа
Best For:
- Полнење преку ноќ за мала дневна километража
- Итно резервно полнење
- PHEV со мали батерии
- Не е потребна инсталација
Ниво 2 Полнење (240V AC)
What is it?: Полнење од 240V штекер (како за машина за сушење) или наменски полнач за ЕВ.
Specifications:
- Моќност: 3.3-19.2 kW (типично 7.2-11 kW)
- Брзина: 12-60 милји досег на час
- Целосно полнење: 4-10 часа
Best For:
- Домашно полнење (најчесто)
- Полнење на работно место
- Јавни паркинзи
- Полнење преку ноќ или дневно
Note: Ова е најдобрата опција за повеќето сопственици на ЕВ. Доволно брзо за дневни потреби, нежно за батеријата и прифатливо за инсталација.
DC Брзо Полнење (DCFC)
What is it?: DC полнење со висока моќност што го заобиколува вградениот полнач на автомобилот.
Specifications:
- Моќност: 50-350 kW
- Брзина: 100-200+ милји за 15-30 минути
- 80% полнење: 20-40 минути
Best For:
- Патувања и патување на долги растојанија
- Брзи надополнувања кога е потребно
- Комерцијални/флони возила
- Кога не можете да полните дома
Important: Полнењето значително забавува по 80% за да го заштити здравјето на батеријата. За најбрзо полнење, планирајте да полните од 10-80%.
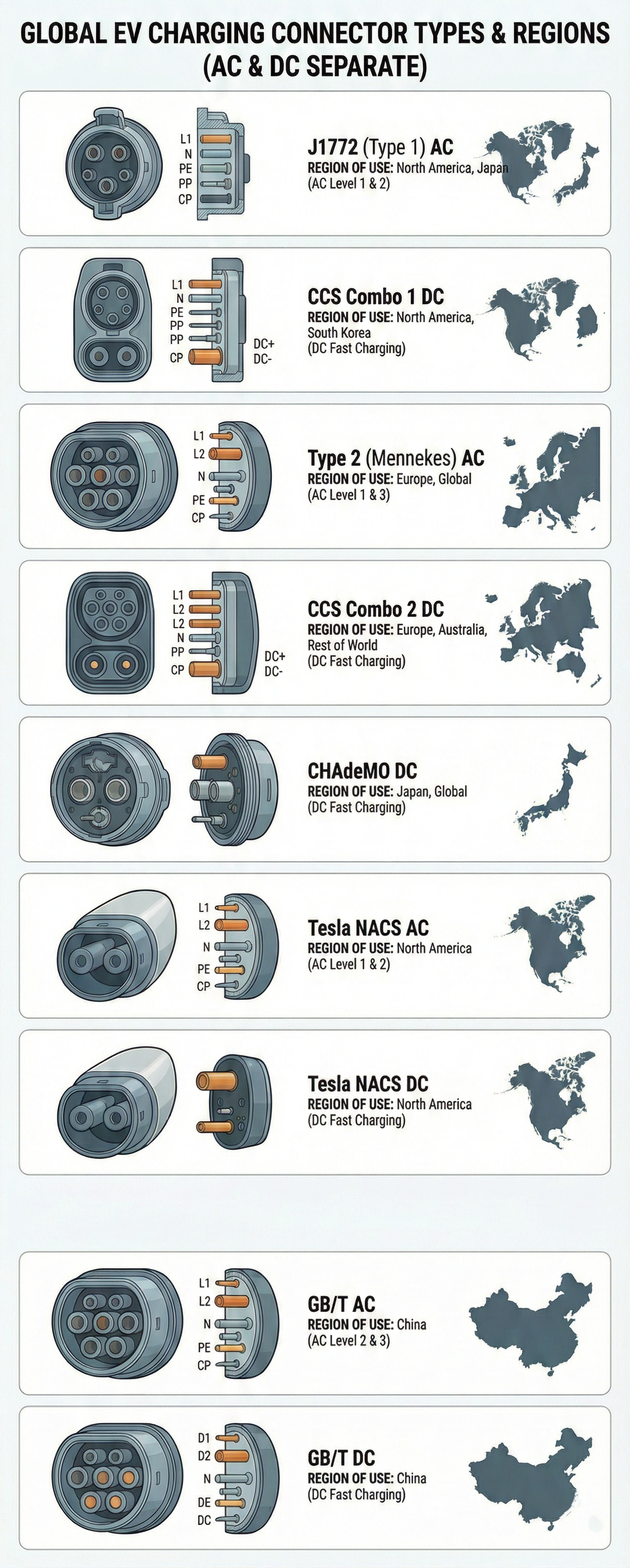
Типови на Конектори по Регион
Северна Америка
J1772 (Tip 1)
Use: Ниво 1 и Ниво 2 AC полнење
Compatibility: Сите не-Tesla ЕВ во Северна Америка
Power: До 19.2 kW (типично 7.2 kW)
CCS Combo 1 (CCS1)
Use: DC брзо полнење
Compatibility: Повеќето не-Tesla ЕВ во Северна Америка
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Го комбинира J1772 со DC пинови за една универзална порта
Tesla NACS (Северноамерикански Стандард за Полнење)
Use: Сите нивоа на полнење (AC и DC)
Compatibility: Tesla возила, станува индустриски стандард
Power: До 250 kW (Supercharger V3)
Note: Ford, GM и други го усвојуваат NACS за идните возила
CHAdeMO
Use: DC брзо полнење
Compatibility: Nissan Leaf, постари јапонски ЕВ
Power: До 62.5 kW (некои станици до 100 kW)
Note: Се исфрла од употреба во корист на CCS
Европа
Type 2 (Mennekes)
Use: Ниво 2 AC полнење
Compatibility: Сите ЕВ во Европа
Power: До 43 kW (типично 7-22 kW)
Note: Европски стандард за AC полнење
CCS Combo 2 (CCS2)
Use: DC брзо полнење
Compatibility: Сите модерни ЕВ во Европа
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Го комбинира Type 2 со DC пинови, европски стандард
Фактори кои Влијаат на Брзината на Полнење
Ограничувања на Возилото
- • Капацитет на вграден полнач (за AC полнење)
- • Максимална стапка на DC полнење (специфично за возилото)
- • Температура на батеријата (ладно = побавно)
- • Состојба на наполнетост (забавува по 80%)
Ограничувања на Полначот
- • Излезна моќност на полначот (kW рејтинг)
- • Споделени кола (моќноста се дели помеѓу автомобили)
- • Капацитет на мрежата на локацијата
- • Состојба на полначот и одржување
Key Point: Вашата брзина на полнење е ограничена од она што е пониско - максималната стапка на полнење на вашето возило или излезот на полначот. Полнач од 350 kW нема да наполни возило со максимална стапка од 50 kW ништо побрзо отколку што би го направил полнач од 50 kW.
Разбирање на Кривата на Полнење
DC брзото полнење не одржува максимална брзина во текот на целата сесија. Наместо тоа, следи „крива на полнење“:
Pro Tip: За најбрзо полнење на патување, планирајте да полните од 10-20% до 80%. Последните 20% траат речиси исто колку и првите 80%, па поефикасно е да застанувате почесто и да полните до 80% наместо да чекате 100%.
Брза Референца
Дневно Полнење: Ниво 2 дома (7-11 kW) - приклучете преку ноќ
Патувања: DC Брзо Полнење (50-350 kW) - застанувања од 20-30 минути
Итно: Ниво 1 од било кој штекер - бавно но работи секаде
Северна Америка: J1772 (AC) + CCS1 или NACS (DC)
Европа: Type 2 (AC) + CCS2 (DC)




























