Compreender o carregamento de VEs pode parecer complicado no início, mas é na verdade bastante simples quando se aprende o básico. Existem três níveis principais de carregamento e vários tipos de conectores usados em diferentes regiões e fabricantes.
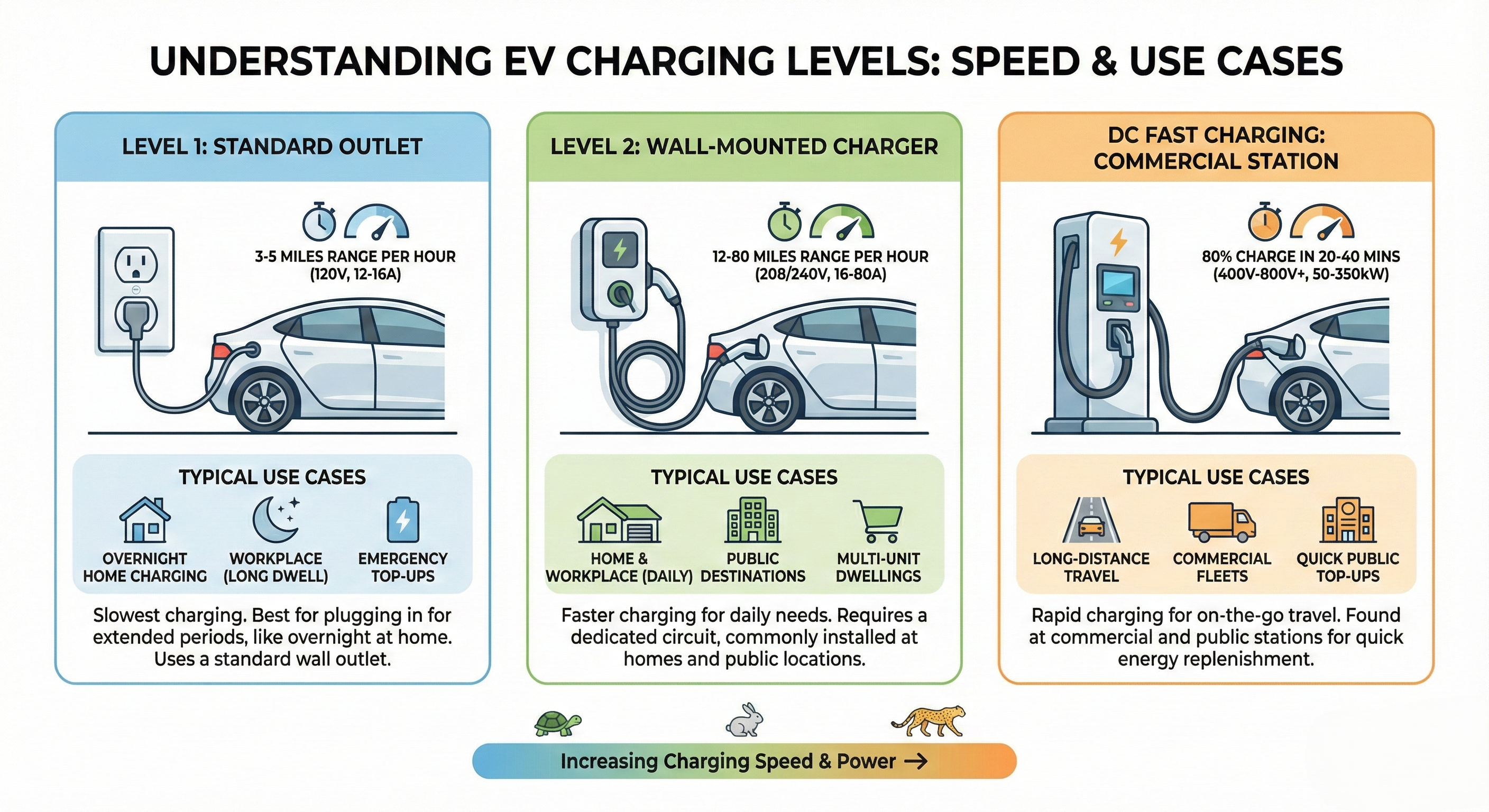
Charging Levels Explained
Level 1 Charging (120V AC)
What is it?: Charging from a standard household outlet (120V in North America).
Specifications:
- Power: 1.4-1.9 kW
- Speed: 3-5 miles of range per hour
- Full charge: 40-50+ hours
Best For:
- Overnight charging for low daily mileage
- Emergency backup charging
- PHEVs with small batteries
- No installation required
Level 2 Charging (240V AC)
What is it?: Charging from a 240V outlet (like a dryer outlet) or dedicated EV charger.
Specifications:
- Power: 3.3-19.2 kW (typically 7.2-11 kW)
- Speed: 12-60 miles of range per hour
- Full charge: 4-10 hours
Best For:
- Home charging (most common)
- Workplace charging
- Public parking lots
- Overnight or daily charging
Note: This is the sweet spot for most EV owners. Fast enough for daily needs, gentle on the battery, and affordable to install.
DC Fast Charging (DCFC)
What is it?: High-power DC charging that bypasses the car's onboard charger.
Specifications:
- Power: 50-350 kW
- Speed: 100-200+ miles in 15-30 minutes
- 80% charge: 20-40 minutes
Best For:
- Road trips and long-distance travel
- Quick top-ups when needed
- Commercial/fleet vehicles
- When you can't charge at home
Important: Charging slows significantly after 80% to protect battery health. For fastest charging, plan to charge from 10-80%.
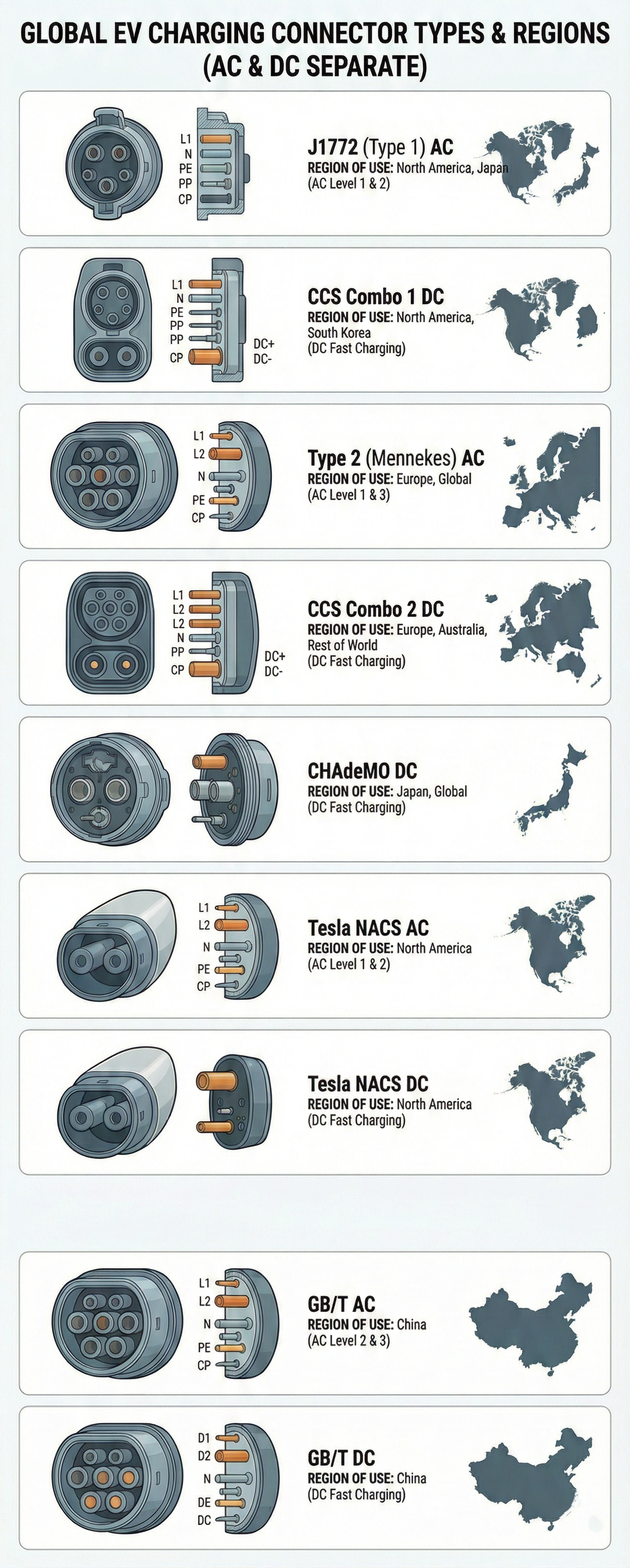
Tipos de Conectores por Região
América do Norte
J1772 (Type 1)
Use: Carregamento AC de Nível 1 e Nível 2
Compatibility: All non-Tesla EVs in North America
Power: Até 19.2 kW (tipicamente 7.2 kW)
CCS Combo 1 (CCS1)
Use: Carregamento rápido DC
Compatibility: Most non-Tesla EVs in North America
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Combines J1772 with DC pins for one universal port
Tesla NACS (North American Charging Standard)
Use: Todos os níveis de carregamento (AC e DC)
Compatibility: Tesla vehicles, becoming industry standard
Power: Até 250 kW (Supercharger V3)
Note: Ford, GM e outros a adotar NACS para veículos futuros
CHAdeMO
Use: DC fast charging
Compatibility: Nissan Leaf, older Japanese EVs
Power: Até 62.5 kW (algumas estações até 100 kW)
Note: Being phased out in favor of CCS
Europa
Type 2 (Mennekes)
Use: Level 2 AC charging
Compatibility: All EVs in Europe
Power: Up to 43 kW (typically 7-22 kW)
Note: European standard for AC charging
CCS Combo 2 (CCS2)
Use: DC fast charging
Compatibility: All modern EVs in Europe
Power: 50-350 kW
Note: Combines Type 2 with DC pins, European standard
Fatores que Afetam a Velocidade de Carregamento
Limitações do Veículo
- • Capacidade do carregador de bordo (para carregamento AC)
- • Taxa máxima de carregamento DC (específica do veículo)
- • Temperatura da bateria (frio = mais lento)
- • Estado de carga (abranda após 80%)
Limitações do Carregador
- • Saída de potência do carregador (classificação kW)
- • Circuitos partilhados (potência dividida entre carros)
- • Capacidade da rede no local
- • Condição do carregador e manutenção
Key Point: Your charging speed is limited by whichever is lower - your vehicle's maximum charging rate or the charger's output. A 350 kW charger won't charge a vehicle with a 50 kW max rate any faster than a 50 kW charger would.
Compreender a Curva de Carregamento
O carregamento rápido DC não mantém a velocidade máxima durante toda a sessão. Em vez disso, segue uma "curva de carregamento":
Pro Tip: For fastest road trip charging, plan to charge from 10-20% up to 80%. The last 20% takes almost as long as the first 80%, so it's more efficient to stop more frequently and charge to 80% rather than waiting for 100%.
Referência Rápida
Carregamento Diário: Nível 2 em casa (7-11 kW) - ligue durante a noite
Viagens: Carregamento Rápido DC (50-350 kW) - paragens de 20-30 minutos
Emergência: Nível 1 de qualquer tomada - lento mas funciona em qualquer lugar
América do Norte: J1772 (AC) + CCS1 ou NACS (DC)
Europa: Tipo 2 (AC) + CCS2 (DC)




























